Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)
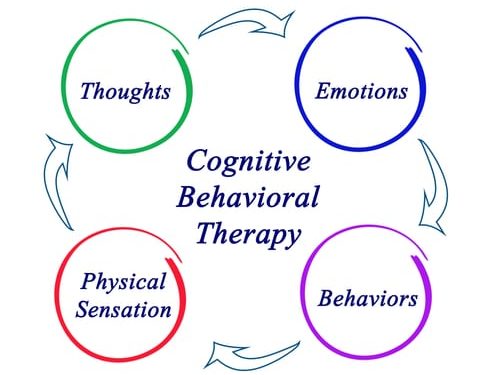
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy is a goal-oriented therapy based on the idea that thoughts, feelings and behaviours are interconnected. If our perception of a situation is negative, this will result in negative emotions and negative behaviours. This treatment focuses on changing patterns of thinking or behaviour that are behind people’s difficulties in order to generate alternative, more balanced ones.
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy will:
- Examine individual patterns of thoughts, emotions and actions
- Help clients make sense of overwhelming problems by breaking them down into smaller parts
- Examine ways to change unhelpful thoughts and behaviours
- Explore strategies to deal with problems
- Provide ‘homework’, in which clients can practice strategies in their everyday life
- Aim to achieve explicitly agreed therapeutic goals within a time-limited framework
- Equip clients with life-long skills which they can continue to practice and develop even after the sessions have finished, making it less likely that their symptoms or problems will return.
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy is used in:
-Stress
-Depression
-Addictions
-Anxiety and Panic Disorder
-Anger Management
-Trauma
-Phobias
-Low Self-Esteem
-Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
-Eating Disorders
How you think about a problem can affect how you feel physically and emotionally. Cognitive Behavioural Therapy can help you to break this vicious circle of altered thinking, feelings and behaviour. CBT aims to get you to a point where you can ‘do it yourself’, and work out your own ways of confronting problems.